
Read the full article in the May edition of C&T magazine.
The advancement of technology has given rise to a new era in beauty and skin care. By using living organisms (bacteria, yeast or fungi) and their derivatives to develop biomimetic products and processes, biotechnology is revolutionizing innovation and sustainability in the beauty industry.
Biotechnology involves the manipulation of DNA and genetic material to produce new ingredients or modify existing ones. In this author’s opinion, not only does it offer the ability to develop and imitate current synthetic or natural ingredients, but its processes have also proven to advance ingredient efficacy and provide better results with a basic set of starting materials. Biotechnology also supports sustainability by reducing fossil fuel energy and deforestation.
Fermentation is the classic example of biotechnology, as it has been used for centuries in food production. The process involves the breaking down of organic material by microorganisms such as bacteria or yeast. For skin care, the fermentation process can produce active ingredients that are highly effective, environmentally friendly and sustainable. The following provides an overview of select examples and their formulating considerations.
Kojic Acid
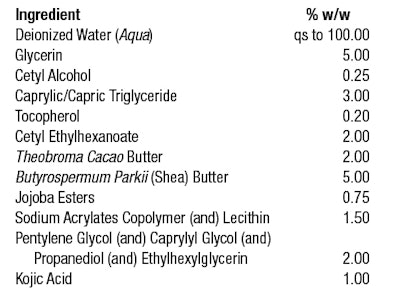
Kojic acid is a naturally occurring substance that can be produced through the fermentation of multiple species of fungi. Notably, it is often an upcycled byproduct from the manufacturing of many popular foods including soy sauce, miso and sake. It acts as a highly effective skin lightening agent and is used to reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation (see Formula 1).
Kojic acid is a white to off-white, water-soluble powder that offers flexibility to skin care formulators. Despite having acid in the name, it is stable within a wide pH range of 3-10. Global regulations vary on formulation concentration requirements with most recommending no higher than 1% in products.
As noted, the process of kojic acid fermentation involves multiple species of Aspergillus fungi. The fungus is grown in a nutrient-rich medium under controlled conditions, temperature, pH and oxygen concentration, and produces kojic acid through a series of complex biosynthetic pathways involving several enzymatic reactions. The resulting kojic acid is extracted and purified for use in skin care, as noted, as a tyrosinase inhibitor — i.e., the enzyme responsible for melanin production in skin. This indirectly prevents additional dark spot generation and reverses signs of skin aging due to inevitable exposure from environmental stress.
Read the full article in the May edition of C&T magazine.
References
- Biossance. (Accessed 2023, Apr 18). Beauty that’s beyond clean. Available at https://biossance.com/pages/sustainability
- Kim, S.K. and Karadeniz, F. (2012). Biological importance and applications of squalene and squalane. Available at https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416003-3.00014-7











