Editor's note: This article has been adapted with permission from our sister brand's, Skin Inc.'s, monthly column, "Jar Deconstructed." In it, the editors review research and commercial reports about an ingredient of interest, along with spa and professional products that apply said ingredient. This month's piece is borrowed from the September 2022 edition.
Argan oil is produced from the kernels of the argan tree (Argania spinosa L.), which is native to Morocco. The region and tree are tightly interwoven, such that argan became the emblem of the lands of the country.1 A. spinosa is believed to be one of the few surviving species of the Tertiary period, some 1.8 million to 65 million years ago.2 This longevity has been attributed to the plant’s ability to withstand the long periods of drought and heat, dry soil and harsh conditions of the Moroccan climate.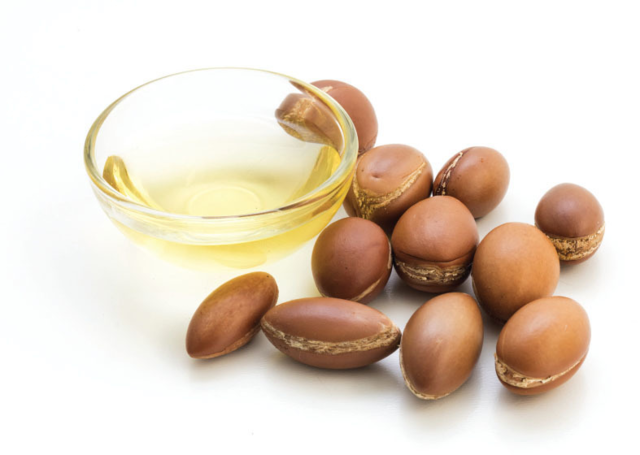
Previously: Inside Ingredients, Ceramides
Argan trees can grow up to 10 meters (∼32 ft.) in height and live for 200 years. At night, the tree attracts atmospheric moisture and store it, spreading it throughout the plant to the roots, which can grow 30 meters (∼98 ft.) deep. When the weather is too extreme, the trees even lose their leaves to avoid evaporation and enter a state of hibernation to emerge when conditions are more favorable.1
Traditional Uses
One of the first reported uses for argan oil was by the Phoenicians (1500-300 B.C.) to fuel lamps. Later, the Berber people are said to have discovered the cosmetic and nutritional benefits of the oil and began to incorporate it into daily life; for example, using it as a skin protectant against the dry climate.1
The argan tree has many uses for both humans and animals. Argan oil was a go-to cure for everything from chickenpox to blood circulation.3 The oil also was, and still is today, used to make almond-argan butter by mixing it with honey and almonds. After the oil is extracted, the remainder of the seed becomes a peanut butter-like paste, which is sweetened and used as a breakfast dip for bread.3 Argan oil also is used in cooking and frying for its rich, nutty flavor and to add flavor to salad dressings or stirred into couscous.4
Animals turn to the argan tree for food. The soft pulp surrounding the nut and seed paste from which the oil is extracted serve as animal feed for sheep, goats, camels and cattle. Argan tree fruits and leaves are also consumed by livestock.4 Goats often climb the trees to reach and eat the fruit, standing among the branches, which can make for a peculiar sight.3
In fact, goat droppings have been cited as a rich source for the precious golden oil—as CNN explained, the hungry animals would climb the thorny argan trees and eat the fruit and leaves but the kernels were not digestible, so those would fall to the ground in droppings. There, enterprising locals collected the kernels to turn into the golden oil.5
The wood from the argan tree trunk is used for firewood and charcoal, and is said to be durable and indestructible by insects, so it can be used for construction and utensils. The small nutshells are burned for cooking fuel.3
Notably, the popularity and demand for argan oil exploded by the 1990s, nearly depleting this natural resource. As such, in 1999, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) recognized the argan tree as a world heritage.6
Active Constituents
Argan oil is mainly composed of fatty acids and phenolic compounds including tocopherols, caffeic acid, oleuropein, vanillic acid, tyrosol and catechol.7, 8 Approximately 29-36% of the fatty acid content is linoleic (omega-6), making argan oil a good source for this nutrient. Oleic acid comprises 43-49% of the fatty acids in argan oil and is known for its heart benefits.8
Argan oil is also rich in vitamin E, a strong antioxidant, which lends itself to healthy skin, hair and eyes. In addition, the phenolic compounds in argan oil are likely responsible for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, Healthline reports, and besides vitamin E, other compounds present, such as CoQ10, melatonin and plant sterols, provide antioxidant activity.8 Argan fruit pulp and argan leaves also contain proteins, peptides, saponins and other chemicals of great interest to dermocosmetics.9
Skin Care Applications
Moroccan women are reported to have long used argan oil to protect their skin from sun damage. Indeed, the antioxidant activity of argan oil has been found to protect against UV-induced free radical damage.10 In relation, a study published in the Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Aesthetic found that argan oil is effective in reducing signs of skin aging by inhibiting melanin synthesis, reducing wrinkles and leaving skin moisturized.11
Argan oil is perhaps most commonly used as a moisturizer, and is often found in lotions, soaps and hair conditioners.10 According to L’Oréal’s website, thanks to its essential fatty acid content (omegas 6 and 9), argan oil helps to restore the skin’s hydrolipidic film, strengthening the skin barrier and limiting water loss.7 A review published in Cosmetics also describes argan oil’s dermatological properties to moisturize the skin, along with antioxidant properties to inhibit the signs of aging—thanks to its relatively high levels of squalene, g-tocopherol and unsaturated fatty acids.13
Some research indicates argan oil can reduce skin inflammation, facilitate healing and improve skin elasticity.10, 14 This could be because linoleic acid deficiency can negatively impact wound healing, so the high linoleic acid content of argan oil may confer properties supporting its traditional use for skin inflammation; notably, however, some other oils that are rich in oleic and/or linoleic acid do not possess the same therapeutic effects.15 Anti-inflammatory and healing effects also may be due in part to argan oil’s antioxidant and vitamin E content, which are reported to ease symptoms of skin conditions such as psoriasis and rosacea.10
Finally, argan oil has been reported, with limited evidence, to treat acne in part by controlling sebum. In relation, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds may reduce the redness and irritation caused by acne, which can help to promote a smoother, calmer complexion. Treatment of stretch marks is another application for argan oil, although again, with limited proof. Yet another traditional use is to treat skin infections, as the oil has shown antibacterial and fungicidal properties.10
In the Spa
With its ability to moisturize skin, protect it from oxidation and reduce inflammation, it should come as no surprise that argan can be found in spa treatments. Though its presence is found primarily in its oil form, you can also find argan kernels in exfoliating treatments.
Kohler Waters Spa in Burr Ridge, Illinois recently launched a number of new treatments, including its "Ohm" Organic Facial (50/80 min., $184/220). This calming and restorative facial features the deep vibrations of singing bowls throughout the treatment. The facial starts with a cleanse and exfoliation with pomegranate seeds and argan kernels, followed by a facial massage. The treatment is concluded with a nori seaweed mask to hydrate the skin.
Argan takes on a moisturizing role in the Moroccan Body Scrub (60 min., 200) at My Moroccan Spa in Dearborn, Michigan. The exfoliating treatment starts with a steam, dry heat and vibration massage in the spa’s pod, which is followed by a massage with a Moroccan black soap. A full body scrub then takes place with Moroccan gloves called "kees." The body is rinsed, and it is then massaged with a Moroccan argan body oil.
Argan is included in countless professional formulations, from moisturizers to waxes and cleansers.
Pevonia includes argan in a number of its Stem Cells Phyto-Elite products, including: Multi-Active Foaming Cleanser, Intensive Serum, Intensive Moisturizer and Intensive Body Corrector. In these products, argan stem cells are utilized to regenerate, condition, protect and de-age. "Argan stem cells can stimulate sluggish dermal stem cells and induce differentiation into new fibroblasts to increase dermal components," noted Christine Dunn, national director of education for Pevonia International.
In Sahara Rose’s Devine Beauty Serum, argan oil is included to replenish lipids. The blend of oils in the serum helps relieve dry, rough patches on the skin and leave it feeling soft.
Argan helps control oil in Bioelements’ Oil Control Mattifier. Along with saw palmetto and sesame seed extract, argan oil helps to balance the complexion. The mattifier is a lightweight cream that absorbs excess oil to keep skin shine-free all day.
For a wax that also calms and moisturizes skin, you can find argan in Lycon’s Pinkini Brazilian Hybrid Hot Wax XXX. The wax is a blend of the company’s traditional hot wax and LYCOtec modern film wax, for both shrink-wrapping performance, extra pliability and ease of use. The low temperature formulation includes titatnium dioxide as well as argan oil, calendula and chamomile to protect, soothe and hydrate delicate skin.
Whish recently launched its Clean Clinical Skin Collection to the professional market, which is comprised of three ranges that differ based on skin type. The sensitive/normal range includes an Argan Stem Cell Exfoliating Cleanser, which is formulated with argan stem cells to rebuild damaged skin, stimulate collagen, moisturize and reduce inflammation.
Conclusion
Standing strong as the mass-extinction meteorite dust settled, the argan tree remains a resilient force against the elements whose survival skills translate to today’s skin care.
References
1. https://www.somemoroccan.com/pages/history-of-argan-oil
2. https://www.arganfarm.com/argan-tree-history/
3. https://apps.cals.arizona.edu/arboretum/taxon.aspx?id=631
4. https://www.kew.org/plants/argan-tree
5. https://www.cnn.com/2016/11/15/africa/argan-oil-morocco/index.html
6. https://www.somemoroccan.com/pages/history-of-argan-oil
7. https://bit.ly/3JmQ7rH
8. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/argan-oil#TOC_TITLE_HDR_2
9. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejlt.201000417
10. https://www.healthline.com/health/argan-oil-for-skin#benefits-of-argan-oil-for-skin
11. https://jdva.ub.ac.id/index.php/jdva/article/view/13
12. https://inside-our-products.loreal.com/ingredients/argan-oil
13. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/8/3/89/htm
14. https://bit.ly/3PJ6Jfq
15. https://altmedrev.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/v16-3-275.pdf
(All websites accessed on July 27, 2022)